
eststo: quietly logit foreign mpg weightĮxponentiated coefficients t statistics in parentheses Regression, harzard ratio in the Cox model, incidence rate ratio, relative risk ratio),

To report exponentiated coefficients (aka odds ratio in logistic Displaying group sizes for categorical regressorsĬoefficients/equations Exponentiated coefficients (odds ratio, hazard ratio).Including a column containing bivariate effects (stack models).Tabulating results from an r-class program.Flip models and coefficients (place models in rows instead of in columns).Advanced LaTeX example: Arrange models in groups.Transforming random-effects parameters of an xtmixed model.

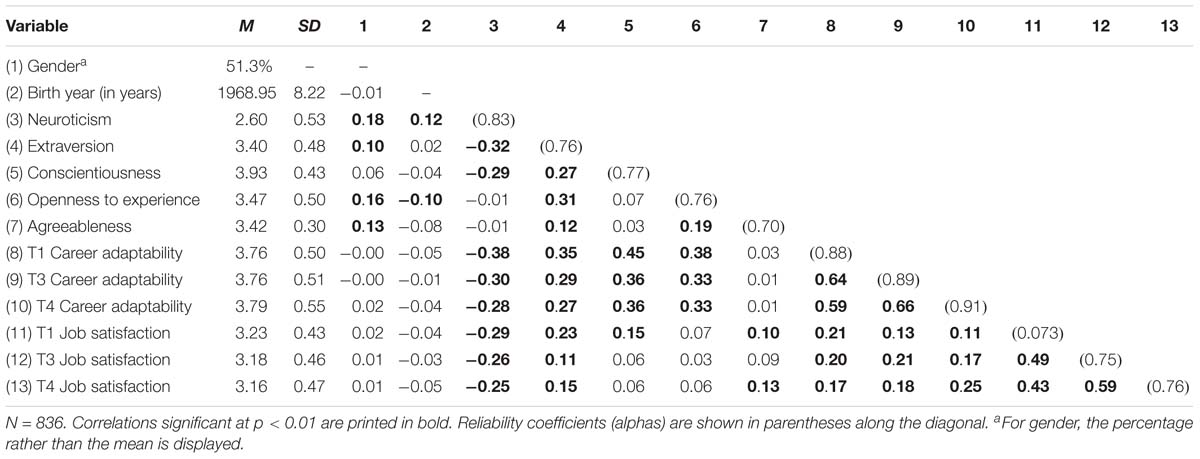
Marginal effects for all outcomes after mlogit.Clean out table after ologit or oprobit.Combining multiple summary statistics in one cell.Rearranging the summary statistics in the table footer.Adding likelihood-ratio test statistics.Display summary statistics only (suppress coefficients).Adding extra rows using the refcat() option.Indicate whether groups of control variables are in the model or not.Table of effects signs, significance stars, or "significant signs".Exponentiated coefficients (odds ratio, hazard ratio).Conclusions: Our results suggest that ambient levels of PM2.5 and ozone can reduce the high-frequency component of heart rate variability in elderly subjects living in Mexico City and that subjects with underlying hypertension are particularly susceptible to this effect. Participants with hypertension had considerably larger reductions in their HF-HRV (high frequency-heart rate variability) component in relation to both ozone and PM2.5 exposure. After adjusting for age and heart rate, we observed a strong decrease in the high frequency component of heart rate variability and the average 24-hour concentrations of PM2.5. Daily 1-hour maximum ozone levels ranged from 47 to 228 ppb. The 24-hour average levels of indoor PM2.5 ranged from 15 to $67\ \mu $.
Results: Of the initial 42 screened participants, 34 (81%) were followed during the study period. Levels of ozone and other atmospheric pollutants were obtained from a nearby automated monitoring station. Indoor and outdoor PM2.5 (particulate matter less than 2.5 mm in diameter) were measured daily at the nursing home.
Background: Suspended particles and ozone have been associated with varying degrees of cardiac autonomic dysfunction Methods: In Mexico City, residents from a nursing home underwent heart rate variability analysis every other day for 3 months.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
